
How Much are House Foundations?įoundations are sometimes charged at a cost per square meter. You can learn more here about the building process. With today’s modern architecture and difficult sites, it is not unusual for all four types of foundations to be used in the one house. In residential construction there tends to be 4 main types of foundation systems: Generally, the deeper the founding depth, the stronger the slab. In addition, the soil report will determine the depth that the concrete rib of the slab is to be founded in the ground. Stronger slabs may have 2 layers of mesh as opposed to the one normally used. The higher the rating the stronger the mesh. For example, SL72 has diameter 7 mm bars, which are on a grid of 200 mm apart. The last digit refers to the spacing of the bars. The first digit refers to the diameter of the bars.

Square mesh is designated by the following sizes SL62, SL72, SL82, SL92 or SL102. The engineer will call up the mesh by the the required size to achieve the needed stiffness for the slab. Steel mesh reinforcement is added for additional strength. The steel is added to give the concrete more strength and stiffness. Stronger slabs may require 32MPA concrete. Standard slabs will require a 20 or 25 MPA concrete. These are called bored piers and are common throughout Melbourne.Ĭoncrete strength is referred to in MPA. If natural ground is particularly deep or the site has uncontrolled fill on it, the foundation will need to be bored through the poor soil and into natural ground. Natural ground is referred to as undisturbed ground on the site. The soil classification will help the engineer determine depth of foundation, the grade of steel to use and strength of concrete to be used.Īll foundations need to be founded in natural ground. P sites include soft or unstable foundations such as soft clay or silt or loose sands, landslip, mine subsidence, collapsing soils and soils subject to erosion, reactive sites subject to abnormal moisture conditions and sites that cannot be classified in accordance with the above classifications. P – Problem soil – Sites with inadequate bearing strength or where ground movement may be significantly affected by factors other than reactive soil movements due to normal moisture conditions. H2 – Highly reactive clay sites, which may experience very high ground movement from moisture changesĮ – Extremely reactive sites, which may experience extreme ground movement from moisture changes H1- Highly reactive clay sites, which may experience high ground movement from moisture changes M – Moderately reactive clay or silt sites, which may experience moderate ground movement from moisture changes S – Slightly reactive clay sites, which may experience only slight ground movement from moisture changes The soil classification considerations for construction are set as follows:Ī – Stable Non-Reactive, Applies Most sand and rock sites with little or no ground movement from moisture changes. These samples are then tested in a laboratory and classified into the categories set out in Australian standard 2870.
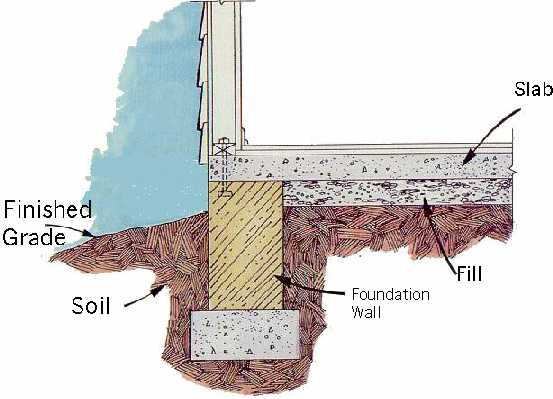
The soil test is done by taking samples of the soil at a number of locations across the site (referred to as bores). The purpose of the soil report is to test the bearing capacity of the soil and what level of reactivity the soil will have to moisture conditions. House foundations are designed by an engineer and take into account the soil that the home is to be built on, the slope of the land and the weight of the building.īefore an engineer can design a footing system for your home they will require a soil report. Who Designs Foundations for Homes and What is Involved? The foundations of the home are the most important component as this will support the entire structure by transferring the weight of the home to the ground. When building a new home there are many components to consider. Understanding House Foundation Types for New Homes as a Cost Consideration


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
